Solution to difficult problems in the use of liquid chromato
011、 Key points for attention in installation, commissioning and maintenance
Chromatographic column is the most important part of liquid chromatograph, and its price is relatively expensive. Please bear in mind that it is a high-grade component in high-grade instruments, and give it enough respect and care. If strong collision and vibration are avoided, even if the chromatographic column is not 100% damaged when it falls from a 1m high test bench to the cement ground, you can't afford 50% of the possible damage. In addition, do not let the column bed dry to avoid freezing in the cold environment.
01
Matching of column head type and stainless steel capillary joint
Chromatographic column is a consumable, not the original equipment of the instrument. If the depth of the joint and the column head do not match, there will be leakage or excessive dead volume. The depth of the joint is longer than that of the column head, so it is not easy to tighten and leak liquid; the depth of the joint is shorter than that of the column head, and there is a gap in the column head, resulting in the birth and death volume, broadening the spectrum band and tailing the peak.
02
Matching conversion of solvents
If the solvent does not match with the mobile phase, it should be converted before use. Especially when the mobile phase contains buffer salt, if the preservation solvent is pure organic phase or organic phase is higher, if the new column is used directly, the buffer salt will crystallize and precipitate in the column, and the new column will be permanently and irreversibly damaged. The preservation solvent of normal phase column is n-hexane. If it is to be converted to HILIC column mode, dichloromethane or ethyl acetate should be used during the conversion due to the poor mutual solubility of n-hexane and methanol acetonitrile.
03
Balance and aging of new column before use
Generally, the balance has been carried out in the factory inspection, but the time from the chromatographic column to the end user is different. It is better to rebalance the chromatographic column before the formal determination by the user. The best way to balance and age together is to run a complete analysis program (including injection) several times until the stability of peak shape, retention time and peak area is observed. The so-called "aging" is a term borrowed from the gas phase in order to achieve the adsorption saturation of analytes in the chromatographic column and the whole flow path of the liquid phase system. For some specific analytes, such as those with molecular weight greater than 1000, the aging time will be longer due to the slow diffusion speed, so the aging can be accelerated by large concentration injection or continuous injection of multiple needles in the same elution cycle.
04
PH application range
It is generally considered that the pH range of silica gel matrix column is 2-8, which is very rough. The type of silica gel, the temperature of use, the type of stationary phase bonded on the surface of silica gel, and the buffer salt have influence on this. The pH tolerance range of silica gel is larger than that of packing with small pore volume and high bonding density. For example, the ultimate xb-c18 column of Yuexu company uses high-quality silica gel, combined with high-density bonding and double sealing tail, so that the maximum pH tolerance range can be increased to 10. Phosphate buffer salt has strong permeability, and has the side effect of accelerating the dissolution of silica gel. Organic hybrid silica gel and silica gel filler coated with hybrid layer on the surface of silica gel. The presence of organic matter enables the pH range to be more than 12. Xtimate series products of Yuexu company belong to this category.
05
Column preservation
For short-term storage (overnight or every weekend), it is better to use the mobile phase (without buffer salt) to minimize the balance time of the next use. It is generally recommended to use pure methanol or acetonitrile for long-term storage of reversed-phase columns. On the one hand, pure organic phase preservation can minimize the hydrolysis of bonding phase, but pure methanol (acetonitrile) will elute the bonded phase which has been hydrolyzed and temporarily adsorbed in the column, thus speeding up the loss process of the stationary phase and shortening the service life of the stationary phase. The pure organic phase has the disadvantage of easy volatilization and drying of the column bed. The use of about 80% organic phase is also a good choice, and can avoid the growth of bacteria. It is strongly recommended to label the column with the preservation solvent.
The CN based column is unstable in organic polar solvents (which may lead to the collapse of the column bed structure) and is suitable for low temperature storage in aqueous phase. The column bed should not be damaged due to freezing of stationary phase. 0.05% sodium azide solution can be added to the chromatographic column suitable for preservation in aqueous solution, such as ion exchange column and water-based SEC column to prevent bacterial growth.
It is recommended that the positive phase column be preserved in the mobile phase used, whether in the short term or in the long term.
The resolution R is related to column efficiency (n), selection factor (?) and capacity factor K ', but not to column pressure. However, the column pressure (P) is still one of the most important parameters in HPLC, because the column pressure reflects the internal conditions of the chromatographic column. Nowadays, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) pumps capable of withstanding 400 bar pressure are very common. If the chromatographic column operates normally at a pressure far below the upper limit, we do not need to pay attention to it. When the column pressure rises close to the upper limit or the column pressure rises abnormally, it often means that the chromatographic column is out of condition and needs to be maintained and remedied in time. In serious cases, the chromatographic column will be scrapped. This section will examine the column pressure problem in detail and propose feasible solutions.
02
2、 Column pressure equation
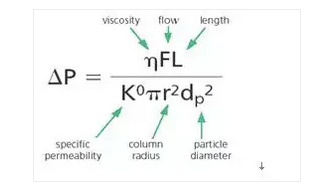
For packed chromatographic columns, the column pressure is directly proportional to viscosity (η), column length (L) and flow rate (f), and inversely proportional to the square of packing particle size (D P) and column tube radius (R). K0 is the specific permeability coefficient, which is about 0.001 for packed bed. The theoretical column pressure under given chromatographic conditions can be approximately calculated by this formula. Only when the actual measured column pressure and the theoretical column pressure differ greatly, can we say that there is a problem with the column pressure.
The viscosity (η) depends on the choice of mobile phase solvent. In order to reduce the column pressure, acetonitrile with low viscosity is preferred instead of isopropanol with high viscosity. Of course, the solvent strength, polarity, solubility of analyte and compatibility with analyte should be considered. The increase of column length (L) can improve the resolution (R), and the increase of flow rate (f) can accelerate the separation, but both of them will lead to the increase of column pressure.
The particle size of filler has a great influence on the column pressure, and the column pressure will be increased by 4 times when D P is reduced by one time. The column pressure of sub-2 μ m packing used in UHPLC is much higher than the upper limit of 400bar of ordinary HPLC pump. Increasing the column temperature factor can reduce the viscosity η and the column pressure accordingly. In gradient elution, the viscosity changes with the change of mobile phase composition, and the column pressure is also in constant change. For the water / methanol mobile phase system, the viscosity and column pressure have a maximum at 55:45.
According to the principle of the same linear flow rate and the same column pressure, the flow rate of 4.6 mm inner diameter column is 1 ml / min, which is equivalent to 0.2 ml / min on 2.1 mm inner diameter column and 5 ml / min on 10 mm semi preparative column. The calculation formula is v = 1.0 ml / min x (inner diameter R / 4.6) 2. Therefore, when changing chromatographic column with different inner diameter, please adjust the flow rate in time to avoid damaging the chromatographic system due to high column pressure.
The drop of column pressure is due to the leakage of the connection of the instrument system. The unstable column pressure is generally considered to be due to bubbles or holes in the flow path. The problem of column pressure related to chromatographic column is the increase of column pressure.
03
3、 Column structure
The most important factors related to column pressure are inlet frit and 1-2cm column packing behind it. There are small holes on the sieve plate which are smaller than the packing particle size, and the gap between the small holes on the sieve plate or the column head packing is partially blocked, which is the main reason for the increase of column pressure. There are the following types of situations:
1. After the packing is broken and used, the filler powder is generated
Packing breakage usually occurs in the process of column loading. If the column pressure is too high or the mechanical strength of the selected silica gel is too low, it can be solved by setting the factory standard for column pressure. The buffer salt with high pH value in the mobile phase dissolves the silica gel and reconstitutes the packing powder, which blocks the sieve plate at the outlet end. In this case, the backwash does not work. Only replace the rear sieve plate, but open the pressurized rear sieve plate, which will affect the column bed Bad influence.
2. Column pressure rise caused by particle blockage and Countermeasures
The sources of particulate matter that may block the gap between the inlet sieve plate (front sieve plate) and the column head packing are: sample (brought in by dust and filter paper during sample preparation), wear of injection valve seal ring, mobile phase (containing solvent itself and entering during preparation), abrasion of pump valve seal ring in liquid phase instrument, buffer salt out (generally caused by gradient operation and salt solvent environment change during sample injection).
Bacteria growing in the mobile phase of water and buffer salt are also a source of particulate matter, which can block the gap between sieve plate and filler. This kind of mobile phase should not be stored at room temperature for a long time and can be stored in the refrigerator.
1) Preventive measures
The filtration of sample (even standard) and mobile phase not only prevents blockage of sieve plate, column head and capillary, but also reduces the wear of key parts of instrument such as injection valve, piston rod and stop valve. The sample and mobile phase are filtered by 0.45 um pore size membrane, and 0.20 um membrane can be used for ultra-high pressure column with less than 2 um filler. The membrane materials include regenerated cellulose, polytetrafluoroethylene, nylon, nitric acid fiber and acetate fiber, which should be carefully selected according to the adaptability of sample solvent and analyte.
Use protective column or on-line filter, the specific installation position is shown in the following figure:
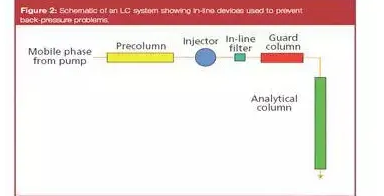
The on-line filter is equipped with replaceable filter pieces, and the filter aperture is generally 2 um and 0.5 um. There are two optional installation positions, between the injector and the chromatographic column, it is effective for both the sample and the particles in the mobile phase; between the pump and the injector, it only filters the mobile phase.
The protective column is a miniaturized chromatographic column, containing a replaceable column core with packing, which is installed between the injection valve and the chromatographic column to prevent the chemical pollution of the chromatographic column, and also has the function of filtering particles.
2) Troubleshooting
Backwash chromatographic column: without connecting the detector, the particles blocked on the front sieve plate are directly flushed out and discharged into the waste liquid bottle. At the beginning, the backwash pressure can be lower than the normal use pressure, and gradually increase the flushing pressure after the particles have been washed out. Sometimes the particles have been embedded in the sieve plate very firmly, so the backwash may not be effective, but the earlier and more frequent backwash are better. In order to avoid clogging, some manufacturers use the front sieve plate with larger pore size (2-5um). In this case, the backflush will flush the packing out.
Changing sieve plate: it is not recommended to change the sieve plate, because it will take away some of the filler stuck on the sieve plate, which will affect the uniformity of the column bed and reduce the column efficiency. However, if recoil can not solve the problem, it can only be done as a last resort, otherwise the chromatographic column will be scrapped.
If the chromatographic column is not connected to the system and the column pressure is still high, it indicates that other parts between the pump outlet and the chromatographic column, including the injector, on-line filter and protection column, are blocked, which can be checked one by one. In order to reduce the dead volume, the capillaries are made as thin as possible and may be blocked.
3. Column pressure rise caused by chemical pollutants and Countermeasures
The sources are also sample, mobile phase and system, but the pollution from samples is the most common, especially when the sample is not pretreated or not enough. Chemical pollutants mainly include compounds with high molecular weight, salts, lipids, waxes, oils, humic acids, proteins and other biological sources.
Pollutants with minimal retention capacity, such as salts, will quickly elute from the column at the dead volume. The detector generally has little response to such substances, sometimes showing interference peaks, baseline fluctuations, spots or even negative peaks.
The pollutants with medium retention capacity will be washed out of the chromatographic column slowly, showing wide peak, baseline steamed bread shape fluctuation and baseline slow drift.
For the pollutants with strong retention, the mobile phase strength is not enough to wash them out of the column, and will gradually accumulate in the column head. Sometimes, the pollutants accumulated in the stigma can act as new stationary relative analytes, causing changes in retention time, peak tailing and peak bifurcation. If no measures are taken, the packing gap will be blocked and the column pressure will rise. The best way is to choose a suitable solvent to wash and dissolve these substances without damaging the filler itself. For example, the accumulated protein pollutants in the polymer column can be washed away with a strong alkali solution of ph13-14, but this method is not suitable for silica gel matrix chromatographic column.
1) Preventive measures:
a. SPE solid phase extraction and other methods were used to remove the pollutants from the column in advance;
b. Connect the protection column. The protection column is the extension of the analytical column. The packing type and particle size should be consistent with the analytical column in order to maximize the protection and not affect the chromatographic performance. A well designed and packed protective column can also increase the separation efficiency of the analytical column. If it is necessary to use different fillers in the protective column for some reason, the stationary phase with weaker retention capacity than the analytical column protected by it should also be selected. At this time, the protective column is completely used to intercept the strong retention substance, similar to the effect of SPE column. When the core protection function of the protection column is exhausted, it can not be said that it can not be reused after cleaning, but the price is low and it is not worth spending this time.
c. Wash and maintain the analytical column frequently.
2) Troubleshooting:
It is recommended to use the following method to clean the reversed-phase column with 100% methanol --- 100% acetonitrile --- 75% acetonitrile / 25% isopropanol --- 100% isopropanol --- 100% isopropanol --- 100% dichloromethane --- 100% hexane. For the 250 mm × 4.6 mm analytical column, the appropriate flushing flow rate is 1 ~ 2 ml / min. Finally, 10 column volume of isopropanol was used for transition, and then returned to the original mobile phase system.
For protein contaminated silica gel column, pure organic solvents such as acetonitrile or methanol can not dissolve peptides and proteins. The formula composed of organic solvent, buffer solution, acid and sometimes ion pair reagent has excellent cleaning effect. For example, trifluoroacetic acid aqueous solution and trifluoroacetic acid / propanol solution are used to regenerate the column; bhadwaj and day test that 100 μ l trifluoroethanol is injected into a 250mm × 46mm column, and the regeneration effect is good.
The recommended method for cleaning silica gel, CN, diol and other normal phase columns is to wash with 20 column volume of 50:50 n-hexane / chloroform, and then wash with methanol, dichloromethane or 100% ethyl acetate. For oil and fat substances, isopropanol can be used for cleaning.
For more related technologies, please consult MS technologies technicians


